Documents
Documents represents the business transactions postings in Contract Accounts Receivable and Payables. The postings are recorded under key called Reconciliation Key.
Document Structure
SAP FI-CA have specialized document structure which is capable of handling very huge volume of data.
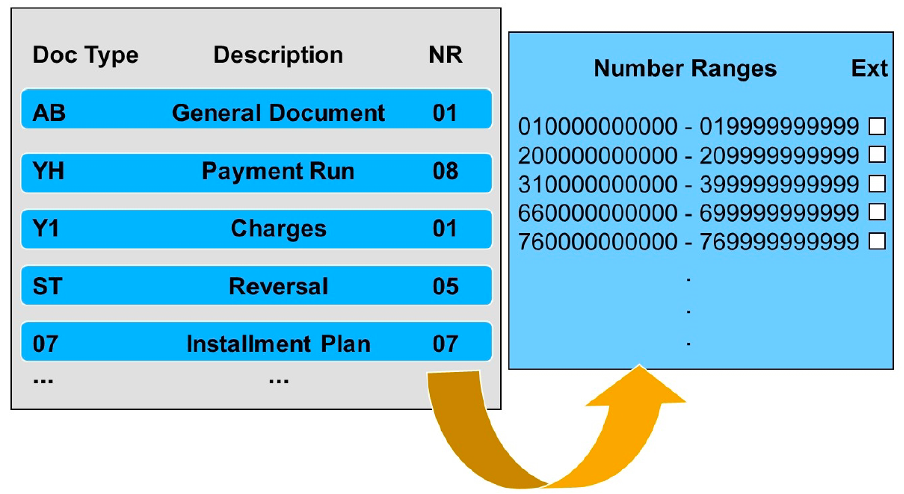
Each document type is identified by a two-digit abbreviation and a description. It classifies the document (receivable, payment). Each document type can be used for manual postings (cash desk) or mass processing (payment run).
Each document type is allocated to a number range to determine the document number intervals. The number range also determines whether document numbers are assigned internally or externally. Document number ranges are specified depending on the volume of the processes.
In addition to the document number ranges for manual postings, additional number ranges must be defined for mass processing business transactions (parallel) like (invoicing, payment run).
The key for the mass processing number range must begin with a letter. Since parallel mass background processes obtain their document numbers from these number range intervals, they must be defined based on the expected data volume and the number of parallel background processes.
"If individual postings of a certain category are frequently executed online (cash desk) and if all postings are executed with the same document type, users may have to wait because all users access the same number range when document numbers are assigned. To reduce or avoid blocking of number ranges, you can allocate multiple number ranges for individual postings to a document type."
Document
- Header
- Business Partner Items
- General Ledger Items
- Repetition Items
- Clearing
Header
The document header contains general data such as
- Document number
- Document type
- Document date
- Posting date
- Currency
- Reconciliation key
- Origin
- Created by
Business Partner Items
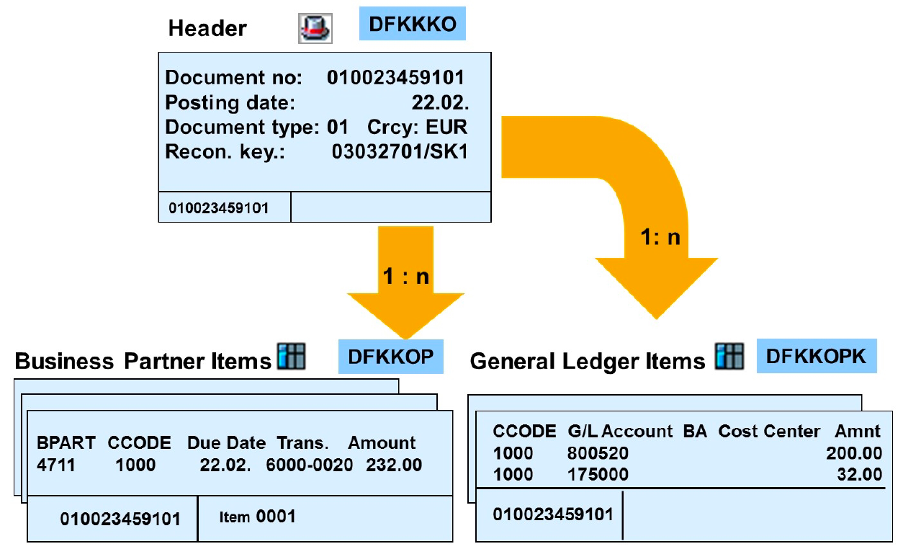
Data relevant for posting is stored in the business partner items.
- Business partner
- Contract account number
- FI-GL receivables account (balance sheet),
- Receivables amount
- Due date
- Clearing information
- etc
General Ledger Items
Data relevant for the offsetting posting is stored in the general ledger items.
- FI-GL revenue account (profit and loss statement),
- Tax account (balance sheet) and
- Tax key
- etc
Offsetting items and tax lines are created automatically, so only the data of the business partner items must be entered by the user.
Repetition Items
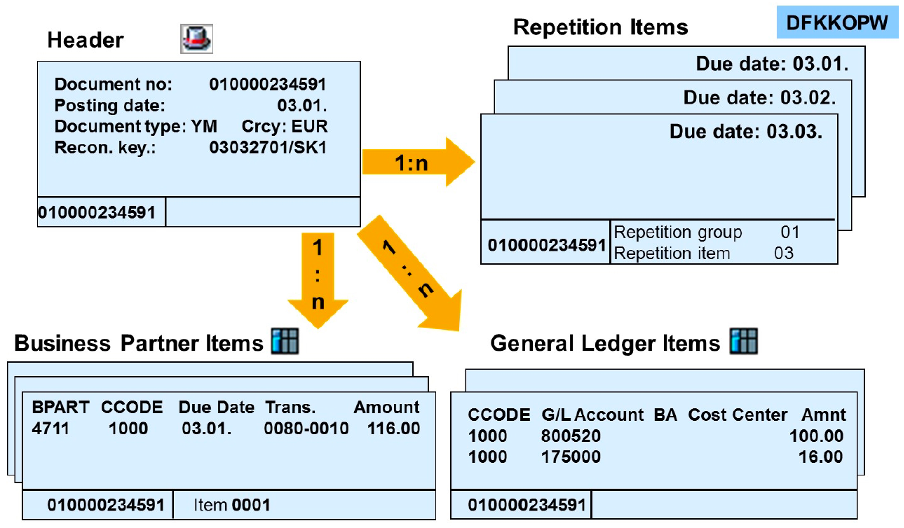
The repetition document is used in installment plans, where the receivable typically consists of many of the same line items that differ only in their due dates.
The repetition item is a fictitious line item in a repetition document, composed of the data of the sample record of an item and the repetition details.
The repetition item of the installment plan is posted statistically, as it refers to a source receivable which is originally posted as a real item.
Clearings
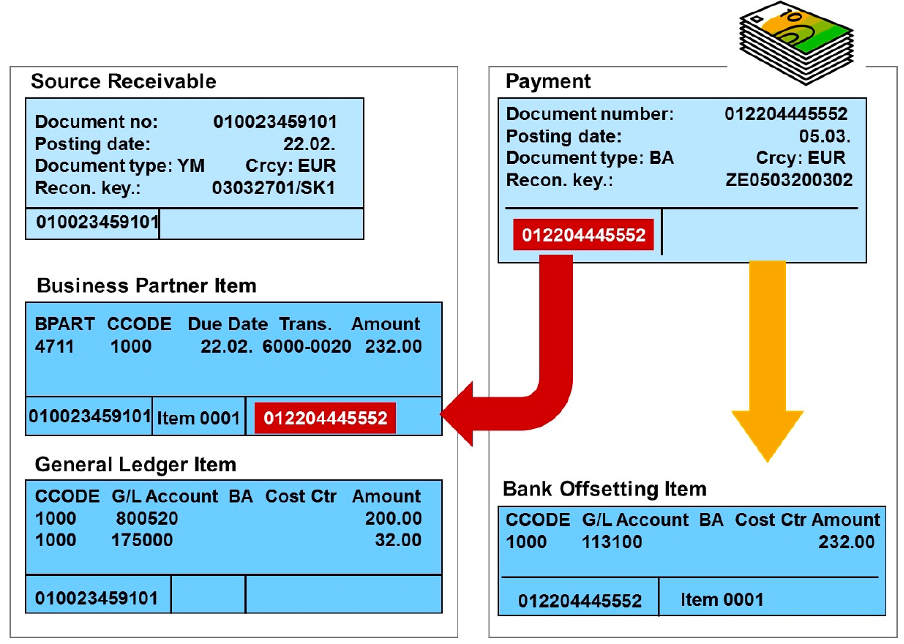
The clearing document (which can be posted for example during incoming payment) consists only of a document header and the offsetting item (No business partner item). The following information is stored in the created offsetting item: • The payment amount • The FI-GL bank account • Information on the cleared document
The document number of the clearing document, the clearing date, and the clearing amount are stored in the business partner item of the cleared document.
This means that both documents are linked as long as the clearing exists. The payment does not maintain a business partner item because all information on the business partner item can be viewed in the linked receivables document.
If clearing is reversed, the connection between the clearing document and the receivable is deleted and the payment document receives a new business partner item with all posting information.
The clearing information is stored in the clearing history of the payment document even if clearing is reversed.
If the payment results only in partial clearing, the item in the source document is split into an open subitem and a cleared subitem, where the clearing information (payment amount and document number) is stored.
Posting Type
-
Real
- is transferred to general ledger
- is included in all processes relevant for general ledger
-
Statistical
- it is not transferred to general ledger
- is relevant for dunning or interset calculation.
- it can be paid or cleared as like real (once paid it gets transferred to general ledger)
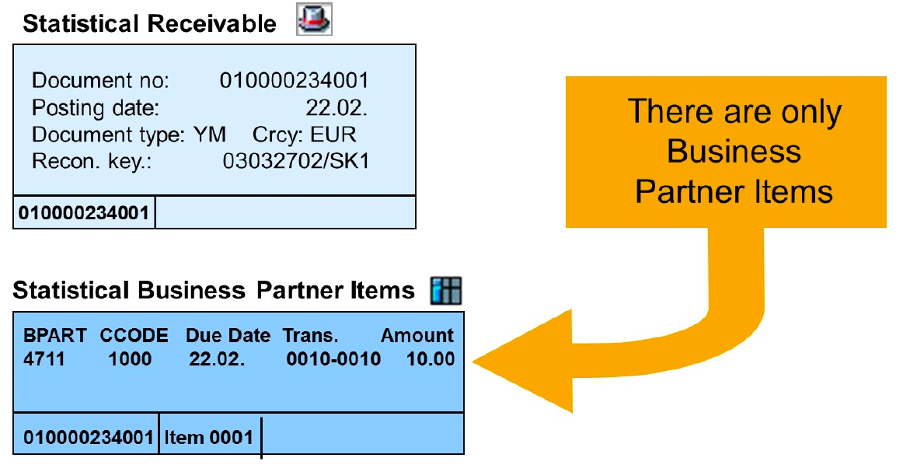
Statistical postings make it easier to deal with uncertain receivables, since these postings are not transferred to the general ledger and, as a result, are easier to reverse if they are not paid.
Typical examples include dunning charges or installment plan items because the underlying source receivables have already been posted in the general ledger.
Statistical documents are comprised of
- Document header
- Business partner items
- Clearing information (In case of clearing)
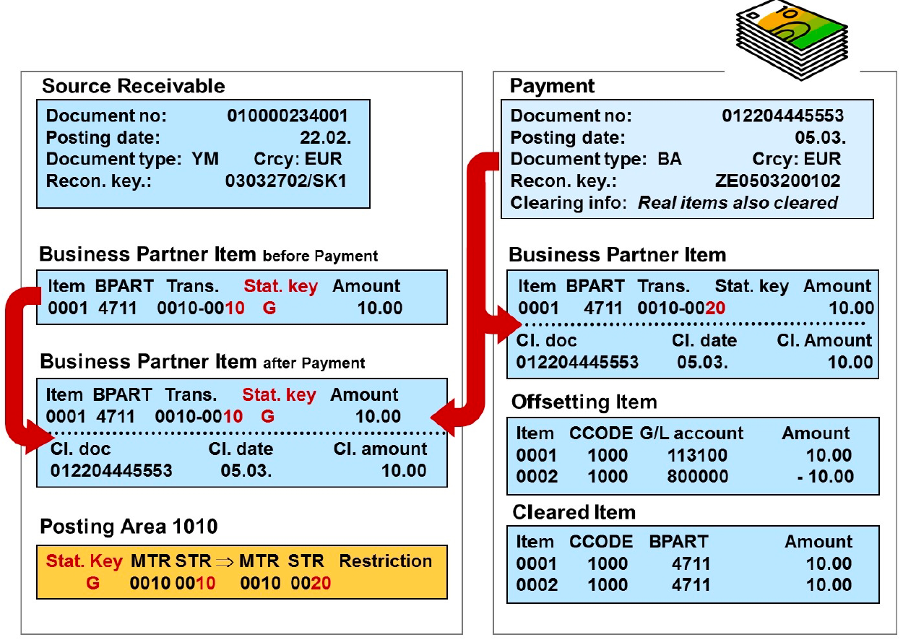
When statistical items are cleared, for example by a payment, the clearing information is stored in the statistical document. A real business partner item (relevant for the general ledger) is created simultaneously in the payment document and cleared immediately.
You need to configure posting area 1010 to determine the main and sub transaction of the automatically generated real item.
Revenue and tax lines are added to the offsetting item as applicable.
Integration with General Ledger
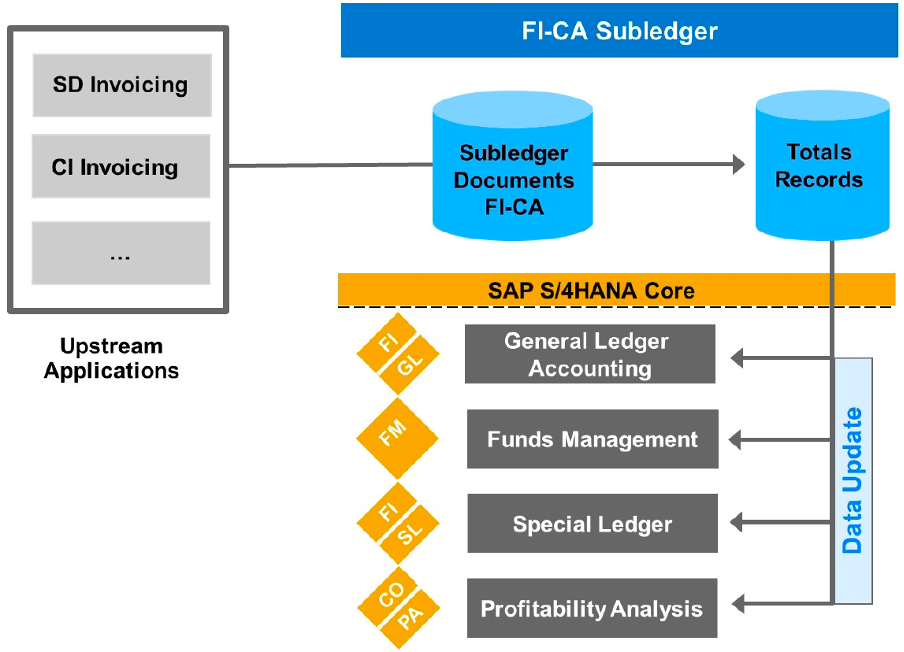
FI-CA serves as a subledger as well as an integrator of accounting data that originates for the most part from various upstream applications and systems. These applications transfer their posting data to FI-CA for further processing. Instead of individually posting each document created in the subledger to the general ledger and controlling, totals records are transferred.
This summarization technique greatly reduces the volume of postings in the general ledger and results in a tremendous performance advantage.
Reconciliation Key
- Key under which totals records are listed
- Gets determined automatically for mass processing
- Default values can be set for manual postings
Reconciliation Key Structure:
- The reconciliation key can be structured for a user group specifically for manual online postings.
- User-dependent and user-independent reconciliation keys can also be proposed for origin keys stored in customizing.
Sample Reconciliation Key Formats:
Payment Lot
XXXXXXXXXXXX
Payment Run
YY DDD NNNNNN PP
Interest Run
YY DDD NNNNNN PP
SD Invoicing
OO YY DDD RRR
YY/DDD --> Year/Day in yearOO --> OriginNNNNN --> Run IDPP --> Job number (Automated determination)
You can use event 1113 to generate/influence default values for the reconciliation key.
FPG4 - Mass closing:
-
The system closes all keys that are not reserved for a specific group of postings, such as postings for a payment run or a payment lot or returns lot.
-
In addition to this, reconciliation keys that are reserved for posting invoicing documents from SD are also closed.
-
If necessary, you can also delete reconciliation keys that have been created but are not used. To do this, select the Delete Unused Open Keys or Delete Unused Closed Keys parameter.
You can use the RFKKABS30 Document Itemization report to select all FI-CA documents posted under a reconciliation key. The totals records are displayed together with all linked FI-CA items.
Totals Records
- Unit which gets transferred from FI-CA to generalledger
- Documents from FI-CA gets consolidated as totals records
- Summarization criteria
- GL account (Receivables, Revenue, Tax)
- CO Object (Cost center, Profit center)
- Comapny code
- Business area
- Posting date
- Currency
- tax code
Skip Summarization:
Summarization can be avoided if required as per business scenario by using the Single Document indicator. If this indicator is set when posting a FI-CA document, a separate item is created in the transfer record for general ledger accounting.
FPG1 / FPG1M: Transfer to General Ledger:
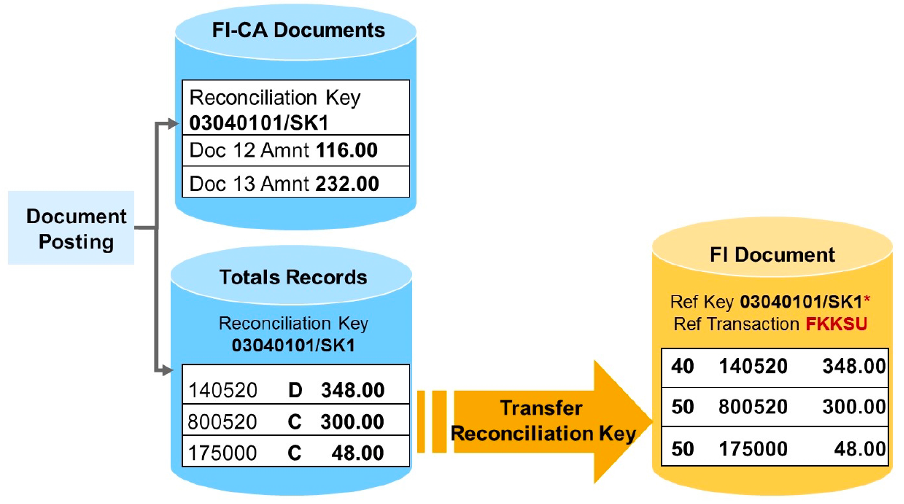
This will transfer the total records into FI-GL. It will create the document in Finance on successful transfer. You must close reconciliation keys to be able to transfer totals records to the general ledger.
Also, you can determine,
- Document type for FI-Gl with posting area 0100
- Debit and credit posting key of the FI-GL document
- Default segment for the segment reporting.
The totals records are saved in the DFKKSUM* tables. DFKKSUMC table have information about total amount and styatus of transfer to General Ledger.
Display document in FI-GL:
You can use transaction FB03 to display the FI document which is automatically created during the totals record transfer.
On the initial screen, choose Document List and enter reference transaction FKKSU and the reconciliation key followed by * in the selection parameters.
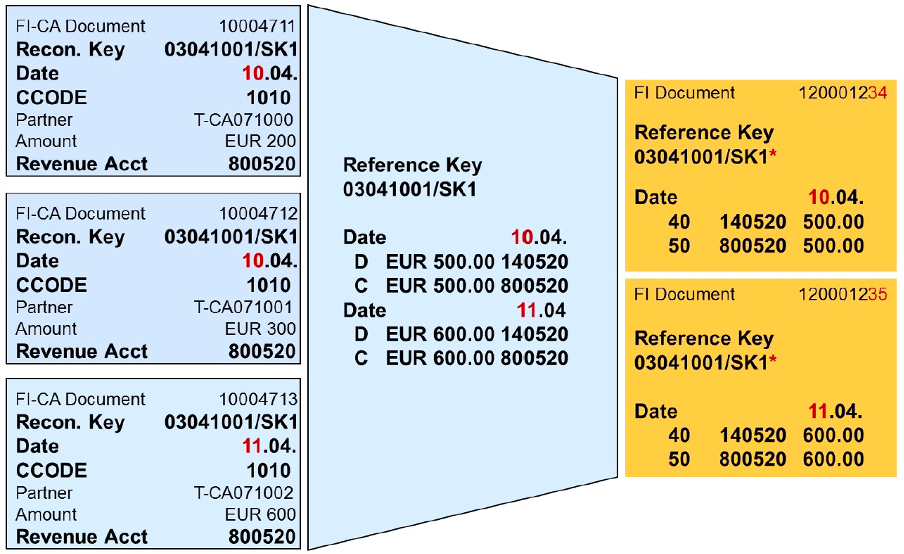
Documents in a reconciliation key are aggregated / accumulated according to posting date and general ledger account.
Transferring totals records with a different posting date creates different FI documents in the general ledger for each posting date.
The reconciliation key is transferred according to the key date.
If the reconciliation key contains documents with posting dates in the future, then the reconciliation key is only partially transferred to general ledger accounting on the key date. The rest of the key is transferred if the future posting date is earlier than or the same as the transfer date.
If the number of lines in the general ledger document exceeds the maximum number of document lines allowed in financial accounting, the document is split and an additional document is created.
The required “zero balance” is posted via a transfer account.
Reconciliation
You should regularly check the totals record transfer for the following issues:
- Reconciliation differences between subledger and general ledger
- Technical issues like database problems or termination of mass processes
You can use the following reports to execute the checks (overview):
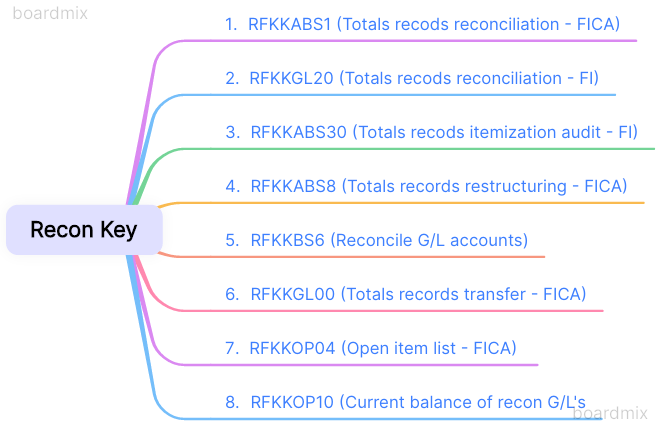
- RFKKABS1 Totals Records Reconciliation in FI-CA
- RFKKGL20 Totals Records Reconciliation in FI
- RFKKGL30 Totals Records Items Audit in FI
- RFKKABS8 Totals Records Restructuring
- RFKKGL00 Totals Records Transfer
- RFKKOP04 Open Item List in FI-CA
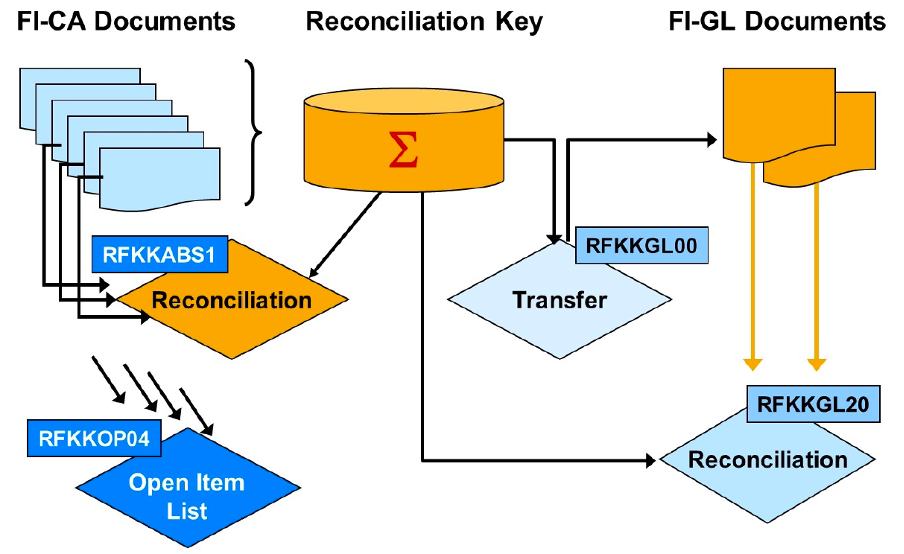
RFKKGL00 report to transfer the totals records to the general ledger.
RFKKGL20 report to reconcile FI-CA and the general ledger.
- Reads the documents that were posted in FI-GL as a result of the FI-CA totals records transfer.
- The documents are then compared with the FI-CA totals records.
- Differences are displayed in color and marked with a red light.
- You can select the corresponding menu option from the output list to correct any differences that occurred (for example, if posting was terminated) and that you were not able to post subsequently. If you select the Correction Run indicator, the system corrects the differences automatically in background processing.
RFKKABS1 report to reconcile inside FI-CA.
- Checks whether the FI-CA postings totals match the totals of the associated FI-CA documents and that the balance of the FI-CA documents is zero.
- Discrepancies between the posting totals and the FI-CA documents are displayed
- The differences can be corrected online or in background processing.
- If FI-CA documents do not have a balance of zero, the corresponding document numbers and reconciliation keys are output.
- These reconciliation keys cannot be exported and cannot be corrected automatically.
RFKKOP04 report to generate a key-date-specific list of all open items in FI-CA. You can use the report during your closing operations (monthly, quarterly, yearly) or for reconciliation purposes.
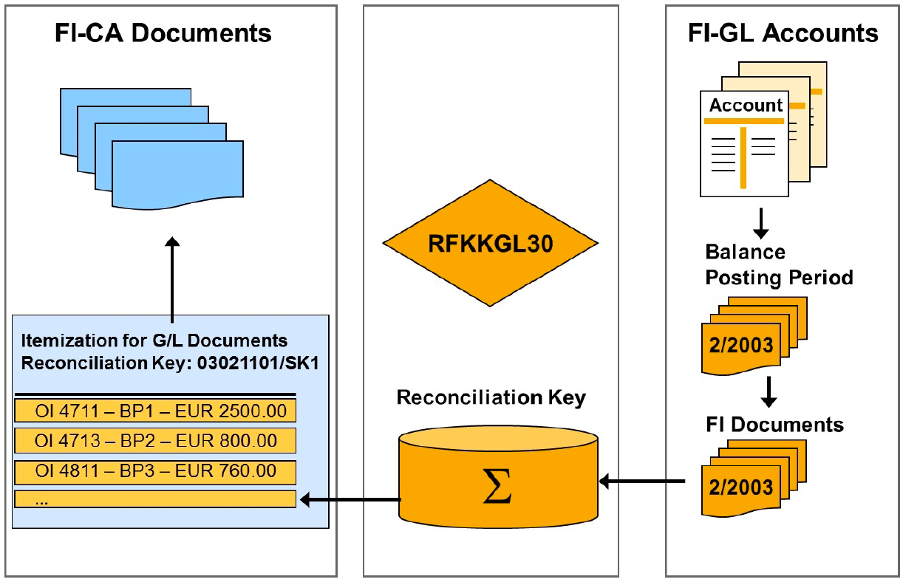
RFKKGL30 report to display the FI-CA documents that have been transferred to the general ledger as totals records.
- The general ledger documents are read according to the selection criteria.
- The corresponding totals records and document lines from FI-CA are selected and sorted.
- Ensure that all FI-CA documents can be audited. This means that you can determine and display the FI-CA items and documents for a general ledger transfer document at any time. A general ledger document can be explained by the items in the subledger at any given point in time.
RFKKABS6 report to reconcile the general ledger accounts.
- The program outputs postings that were transferred to the general ledger.
- The postings are displayed as a balance overview or as line items with the corresponding posting date and, if available, an alternative posting date.
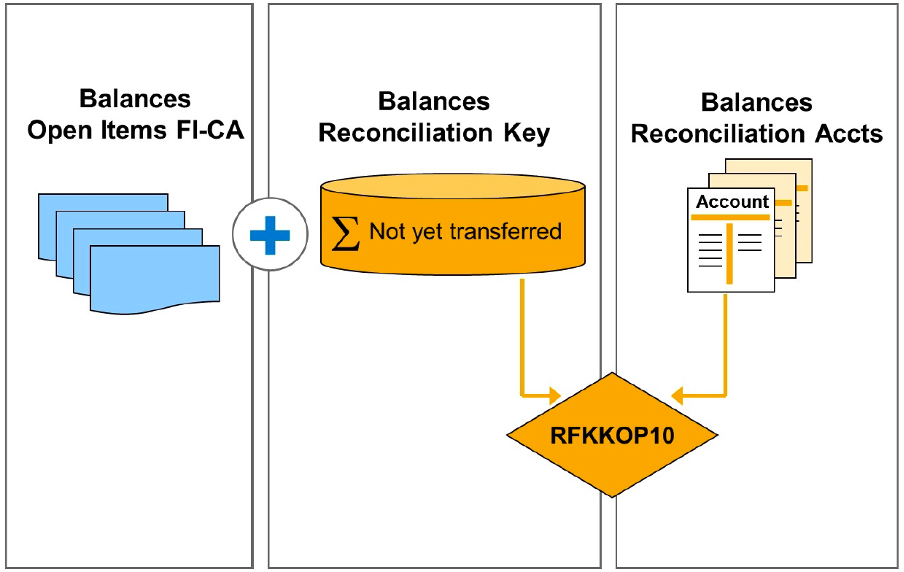
RFKKOP10 report to reconcile the current balance for reconciliation accounts and clearing accounts.
The following balances are calculated:
- Balance of current open items in FI-CA
- Balance of current reconciliation accounts in FI-CA and FI-GL
- Balance of reconciliation keys in FI-CA that have not yet been transferred
- Balance of adjustment totals records in FI-CA that have not yet been transferred
Segement Reporting
The segment is standard account assignment object in FI-GL to create evaluations for entities below the company code level. The object of segement reporting is to give the detailed look at various business activities of a braad based enterprise. ˜ Alternative account assignment to segment:
- Profit center
- Business area
- Profitibility segment
- User defined field
Segment reporting meets the requirements of international accounting principles, such as:
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
- United States General Accepted Accounting Principles (US-GAAP)
According to IFRS, a segment is an area of a company that has the following characteristics:
- It carries out business activities that generate revenue, for which expenses can be incurred (including transactions with other areas of the same company).
- Its operating profits are regularly inspected by the main decision-maker with regard to the allocation of resources to this segment and the evaluation of its profitability.
- It has no corresponding financial information
Displaying the profit and loss statement by profit center, business area, or segment is never problematic because the positions that have an effect are always provided with unique corresponding objects by the original controlling object.
However, if a balance sheet is to be created for one of these objects, the problem is that the line items in FI-GL like receivables and taxes cannot be split accordingly.
In classic FI-GL, the additional closing activity Financial Statement Adjustment breaks the receivables, payables, and taxes down into the additional account assignments Business Area and Profit Center, which are stored in the general ledger account items.
In the new FI-GL, the Document Splitting action replaces the financial statement adjustment. Document splitting is only relevant if you want to enter a further characteristic, such as a segment on the balance sheet in addition to the company code.
In terms of compatibility of FI-CA with the FI-GL document splitting scenario, the following general statements apply:
- A customer who uses FI-CA and splits documents in FI-GL must ensure that the required characteristics can be added in FI-CA.
- Segments are derived according to FI-CA-specific rules whose splitting logic differs in FI-GL.
- For reconciliation reasons, FI characteristics cannot be added to FI documents from FI-CA because reconciliation in FI-CA takes place at account assignment level (business area, segment, profit center).
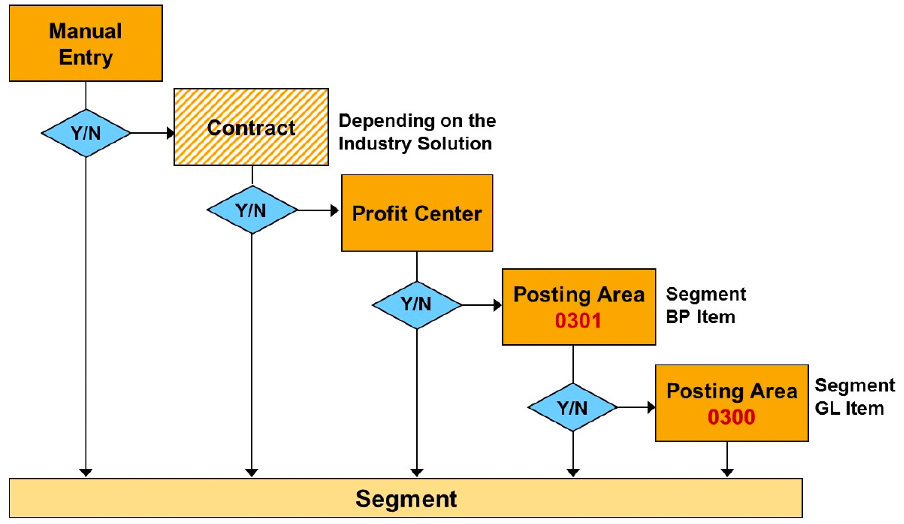
The segment of a FI-CA document for subsequent postings (payment of invoice) is derived automatically from the source document. The segment of a FI-CA document for non-subsequent postings (payment on account) is derived as follows:
- Manual postings: You can enter the segment directly.
- Automatic postings (Payment of invoice): the segment is derived from contract or profit center (if used) from source document.
- Automatic postings (Payment on account): you can use posting area 0301 to derive the segment for BP items.
- Automatic postings (Tax account and Bank account): you can use posting area 0300 to derive the segment for GL items.
Sample Transaction Codes
| Transaction Code | Description |
|---|---|
| FPE1 | Post Document |
| FPE2 | Change Document |
| FPE2M | Mass Document Change |
| FPE3 | Display Document |
| FPE4 | Display Dcoument Changes |
| FS00 | Disppay G/L Master Data |
Sample Perocess Flow
Processes in SAP FI-CA
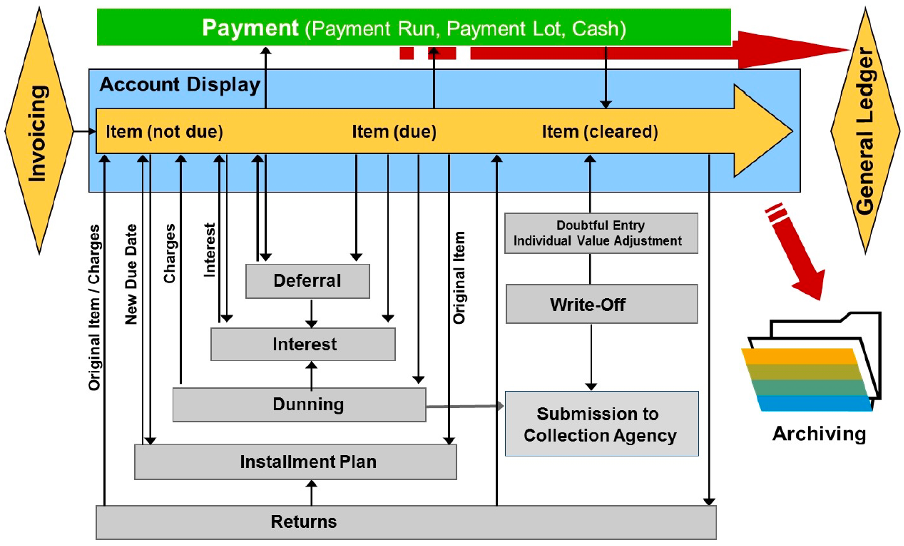
- Documents can be posted as receivables (usual form) and sometimes as payables.
- Documents can be posted in invoicing (usual form), dunning, or returns processing.
- Documents can be posted manually as well.
- Cleared and open items are regularly compressed and transferred to the general ledger.
- Cleared and open items can be displayed using the account balance display.
- Cleared documents that have expired can be archived.
Payments can be initiated by a business partner (payment lot) or by company (payment run). Payments clear open items and can be displayed using the account balance display in customer account.
In the context of returns processing, cleared payments are reset, the source receivables are recorded as debit items, and return charges are applied. These charges might include bank fees transferred to the business partner or charges levied directly by the company.
In dunning processing within fi-ca, overdue payments from cash payers or blocked transactions from direct debit payers may undergo the dunning process. This involves the possibility of applying dunning charges or accruing interest on outstanding balances.
Following the dunning run, items may be forwarded to external collection agencies. Payments such as interest and external collection agency charges can be posted.
Interest can be calculated either automatically in the invoicing and dunning run, or manually. Interest can be calculated for open and cleared items, as well as for debit and credit items. Interest documents are posted.
Interest calculation can occur automatically during invoicing and dunning run or manually. Interest may be calculated for both open and cleared items, and also for debit and credit entries. nterest documents are posted accordingly.
Open documents can be deferred manually. A deferral can take place automatically in returns processing. The original due date is retained in the case of a deferral. If the deferral date is reached and the item is still open, the original due date is used again for further business processes.
Open documents can be integrated into an installment plan. Interests can be calculated using the installment plan. The interest receivable is integrated into the installment plan.
Overdue items can be entered as doubtful, adjusted individually, or written off.
Customizing
SPRO
SAP Reference IMG
- Financial Accounting
-- Contract Accounts Receivable and Payable
--- Basic Functions
---- Postings and Documents
Number Range Object
Posting Areas
| Posting Area | Description |
|---|---|
| 0010 | Determine the main and sub transaction of the automatically generated real item. |
Tables
| Table | Description |
|---|---|
| DFKKKO | Header Data in Open Item Accounting Document |
| DFKKOP | Business Partner items in contract account document |
| DFKKOPW | Items in contract account document (Repetition) |
| DFKKOPK | G/L Account items in contract account document |
| DFKKOPWH | Withholding Tax Data for Business Partner Item |
| DFKKRAPT | Clearing/Reversal History (Line Item Level) |
Authorization Objects
Possible values
Function Modules / BAPI
| Function Module | Description |
|---|---|
| FKK_CREATE_DOC | Buchen einzelnen Beleg im Massenkontokorrent |
| FKK_CREATE_DOC_AND_CLEAR | Buchen einzelnen Beleg im Massenkontokorrent mit Ausgleich anderer Belege |
| FKK_CREATE_DOC_MASS | Buchen Beleg im Massenkontokorrent (Massendaten) |
| FKK_CREATE_DOC_MASS_AND_CLEAR | Buchen Beleg mit Ausgleich im Vetragskontokorrent (Massendaten) |
| BAPI | Description |
|---|---|
| BAPI_CTRACDOCUMENT_CREATE | You can use this method to post FI-CA document. |
| BAPI_CTRACDOCUMENT_CHANGE | You can use this method to change FI-CA document. |
| BAPI_CTRACDOCUMENT_GETDETAIL | You can use this method to get details of FI-CA document. |
| BAPI_CTRACDOCUMENT_EXISTCHECK | You can use this method to check existance of FI-CA document. |
Events
| Event | Description | Sample Module |
|---|---|---|
| 0010 | Posting: Document Complete (No Number) | |
| 0020 | Posting: Document/Clearing Completed (No Number) | |
| 0030 | Posting: Document Number Assigned | |
| 0031 | Posting: Document Number Assigned for Additional Document | |
| 0032 | Posting: Create Additional Line Items | |
| 0040 | Posting: Check Open Item Accounting Item | |
| 0041 | Posting: Add Open Item Acctg to Cash Mgmt Data | |
| 0042 | Posting: Set OI Accounting Item Clearing Restrictn | |
| 0043 | Posting: Add OI Accounting Item Business Place | |
| 0044 | Posting: Add Open Item Acct Item CFOP Number | |
| 0045 | Posting: Determine Last Recipient | |
| 0046 | Posting: Check Variable Withholding Tax Data | |
| 0050 | Posting: Check G/L Item | |
| 0060 | Posting: Check Document Header | |
| 0061 | Posting: Check Complete Document, Set Customer Fields | |
| 0062 | Posting: Exchange Posting Date | |
| 0063 | Posting: Include Document in Collective Bill | |
| 0064 | Posting: Authorization for Contract | |
| 0066 | Posting: Add Expense/Revenue Account for Cash Flow Analysis | |
| 0067 | Posting: Exchange Tax on Sales/Purchases Code | |
| 0070 | Posting: Check if Reversal Permitted | |
| 0071 | Posting: Check if Clearing Reset is Permitted | |
| 0072 | Posting: Reversal in Alternative Fiscal Year | |
| 0080 | Posting: Determine Offsetting Company Code | |
| 0081 | Posting: Set Segment Account Assignment | |
| 0082 | Posting: Determine Segment from Profit Center | |
| 0085 | Posting: Additional Industry Data for Rounding Items | |
| 0086 | Posting: Industry Grouping Key for Rounding | |
| 0090 | Posting: Data Rollback | |
| 0100 | Posting: Charge for Tax-Free Posting (Italy) |
Package
FKKB
Function Groups
| Function group | Program | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FKB0 | SAPLFKB0 | FI-CA posting interface |
| FKK_BOR_DOC | SAPLFKK_BOR_DOC | BAPI: FI-CA Document |
==============================
Updates in progress - Stay Tuned..!!!